Debridement and Chronic Wound Managment
MAY IS DEBRIDEMENT AND CHRONIC WOUND MANAGEMENT MONTH For this month's WoundSource Practice Accelerator series, we are providing education on a variety of topics related to chronic wound debridement. Scroll below to read this month's white paper and articles, to print out our quick fact sheet, and to sign up for this month's webinar.
Upcoming Webinar
Devitalized Tissue: What to Look For
Tuesday, May 24Kelly McFee, DNP, FNP-C, CWS, CWCN-AP, FACCWS, DAPWCA
Wound debridement is an essential component of wound care and is integral to healing in chronic wounds to remove devitalized tissue from a wound. This removal of devitalized tissue is essential to promote granulation tissue formation and epithelization for wound closure. There are different kinds of devitalized tissue that may be debrided in a variety of ways. The type of debridement selected may be dependent on the characteristics of the wound, the clinician’s skill level, the treatment settings, and the patient’s needs at the time of care. By the end of this webinar, wound care professionals will be able to:
- Identify devitalized tissue types
- Determine when debridement is appropriate
- Understand the different types of debridement and when they may be appropriate
- Discuss examples of the different types of debridement
White Paper
Understanding Debridement and Making the Right Choice for Each Patient
<p>Debridement, defined as the removal of necrotic nonviable tissue, infected tissue, or foreign debris, is an integral component of wound bed preparation and is used to promote healing. Understanding the different categories of debridement helps wound care professionals choose the most appropriate type for each individual patient's wound. This white paper provides a comprehensive overview of debridement and discusses the importance of this procedure in wound care.</p> ...Fact Sheet
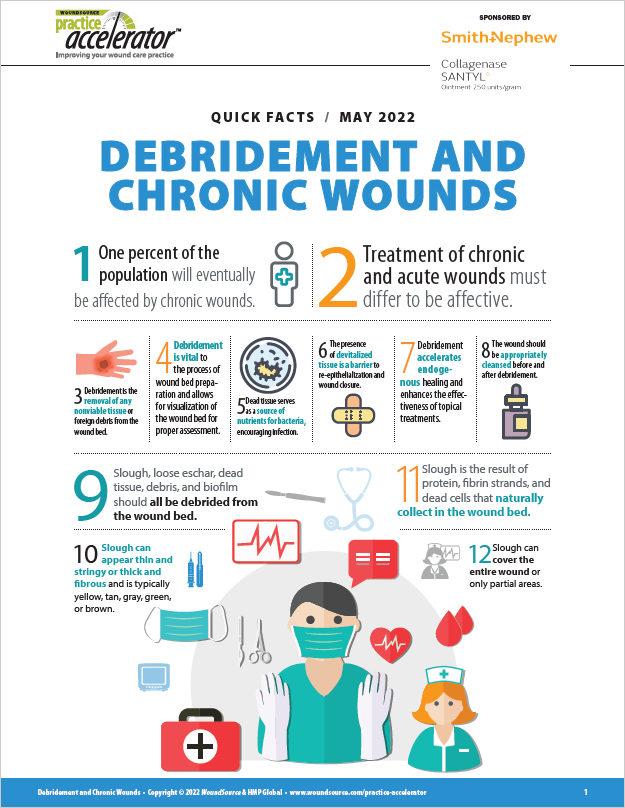
Quick Facts - Debridement and Chronic Wounds
In patients with stalled, nonhealing chronic wounds, meticulous wound bed preparation is essential. A key component of this preparation is debridement, which consists of the removal of any nonviable tissue or foreign debris from the wound bed. Nonviable or necrotic tissue impairs wound healing. By removing this tissue, debridement helps move the wound along the healing trajectory, for optimal clinical results. Wound care professionals will appreciate this useful resource, which contains importan...Featured Articles
Debridement: Why Is It So Important?
Effective wound management often requires attending to multiple aspects of the wound itself, including properly preparing the wound bed and managing moisture and exudate, among other facets of wound care. Tissue viability is another crucial aspect of wound management. Unfortunately, many types of wo...
Read MoreProviding Care During a Pandemic: Patients With Comorbidities
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted many aspects of patient care and medical practice. Changes have ranged from supply chain adjustments to transformations in patient interactions. Many of these practices may be standard for the foreseeable future. Although many medical professionals have ...
Read MoreInvolving Patients in Care: Debridement Considerations
Patient-centered care is a philosophy that stresses communication, collaboration, and health promotion while also respecting patients' expectations, autonomy, and values. It is at the heart of global efforts to enhance the delivery of safe, high-quality, and cost-effective health care. Patients who ...
Read MoreWound Assessment: What Does This Wound Need?
For the wound healing process to be successful, it must pass through four stages: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling or maturing. Wound healing requires inflammation, but it can be detrimental if it is persistent or encouraged by other factors, such as infection. It is during th...
Read More